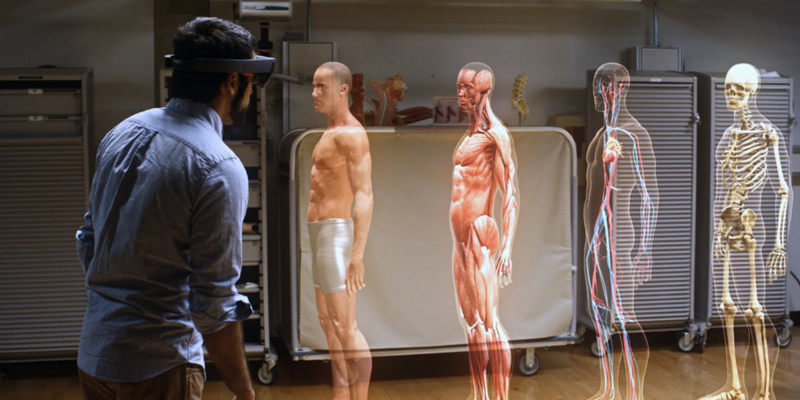
Many industries have come on leaps and bounds thanks to great technological advancement, but none more so than the medical industry. Diagnostic medicine, surgical procedures, and even patient administration have all been fundamentally transformed thanks to new technologies.
And with the advent of Virtual Reality (VR), we are truly on the cusp of something special.
In this article we take a look at how Virtual Reality in medicine is already being utilized to help make existing healthcare procedures and practices more effective and efficient.
Virtual Reality, along with its sister technology of Augmented Reality, will make up a global marketplace projected to generate $150 Billion by 2020. Its impact within the healthcare industry is likely to be far reaching and game changing. From altering how young doctors are trained to improving how certain illnesses are diagnosed and treated, the potential of VR is incredibly exciting.
What Is Virtual Reality?
The simple definition of Virtual Reality in this context is a piece of technology that allows the user to experience a feeling of ‘near-reality’.
As we typically understand the world around us via our senses and perception systems, VR technology has been developed to mimic the sensory outputs of the real world, presenting the user with a computer generated virtual environment that would be perceived as being authentic.
How Much Does It Cost to Develop a VR App?
By the time the bells ring out signalling the start of a new year, the total number of VR users will exceed 43 million. This is a market on the move, projected to be worth $30bn by 2020.
When the user explores and interacts with this virtual environment, their brain will process the visual, auditory, and tactile information as if it were taking place in the real world.
In short, Virtual Reality leverages a number of hardware and software technologies to achieve its goal of fooling the user’s brain into perceiving the virtual world as real. And with applications in entertainment, commerce, and a wide variety of technical industries, we can expect a seismic change to the way in which we work, communicate, and learn.
Both doctors and patients can use devices such as specialist VR headsets or smartphone viewers such as Samsung Gear VR or HTC Vive to leverage this technology and add value to their training, diagnosis and treatment.
Virtual Reality Medicine for Patients
VR technology has already changed the way in which several treatments are administered, and it has proven itself especially effective in dealing with particular social cognitive disorders such as phobias and anxiety.
Treating Phobias with Virtual Reality
When the South African psychologist James Taylor developed Exposure Therapy in the 1950s, the idea that advanced technology could be utilized to treat patients’ pathological fears probably seemed like science fiction.
The therapies pioneered by Taylor required patients to place themselves in real situations that caused anxiety, allowing the psychologist to then treat them. The goal of this treatment was to progressively teach the brain’s emotional centre (the limbic system) that the situation eliciting the fear and anxiety was not actually threatening.
Virtual Reality technologies make this entire process more efficient and effective. The therapist administering the treatment can carefully control the entire experience according to the needs of the patient. For instance, if the person is an arachnophobic (scared of spiders) then the therapist, with the click of a mouse, can place a virtual spider in front of the patient.
For anyone who has never truly experienced a phobia, it can be hard to understand how a virtual environment can ever really replicate the experience of confronting a fear in real life. Can a virtual spider resemble a real spider in such a way that VR technology is helpful?
The fact of the matter is Virtual Reality therapy works, not because of the realism of the spider, but rather the way in which the brain’s pathways are activated in people suffering from phobias in a virtual environment. Those who aren’t afraid of spiders are able to pick up on the subtleties of the virtual world, informing them that this particular arachnid isn’t actually real nor a threat.
On the other hand, phobics will look for what they perceive to be crucial for their survival in that moment. The appearance, movement, and characteristics of the virtual spider will be enough to trigger a powerful emotional response, therefore allowing the therapist to set about helping the patient correct this response.
Treating Autism with Virtual Reality
Beyond helping patients overcome their fear of creepy crawlies, VR has also proven effective in treating young people on the autism spectrum. For many suffering from autism, they will display symptoms of anxiety and fears associated with social situations.
Trials undertaken at Newcastle University have proven to be very successful, as it allows people with autism the opportunity to visualize certain situations via VR technologies, rather than try to use their imagination, something they find very difficult to do.
It also allows parents the opportunity to observe their child working with a therapist and pick up on techniques that can help them when the real-life situation arises.
With phobias and social anxieties becoming more and more common, existing and developing Virtual Reality medical applications can help make treatment increasingly accessible and successful.
In addition to treating social and mental disorders, Virtual Reality has also been effective in physical therapy for patients with burn injuries, brain damage rehabilitation, and eye defects.
Virtual Reality Medicine for Doctors
When it comes to healthcare practitioners, there are dual benefits to utilizing Virtual Reality for medicine:
- Firstly, training and education is enhanced, allowing trainee doctors to step away from their textbooks and immerse themselves in the situations they will one day be facing.
- Secondly, the VR technology will allow doctors to diagnose and treat conditions more effectively than ever before.
Medical Training & Education Applications of VR
One of the most obvious applications of Virtual Reality in medicine is that of surgical simulations. Prospective surgeons can learn their trade without the moral or ethical dilemmas of treating real-life patients as they train.
Traditionally, surgeons would use surgical simulators to learn the basic skills required for laparoscopic surgery, allowing them to perform and perfect specialist maneuvers. However with the strides being made in VR technology, the simulators being used are now able to mimic entire complex surgical procedures with specific variations to anatomy or pathological conditions thrown in for good measure. These VR systems are much more immersive thanks to the visual, auditory, and tactile feedback modern technology provides.
And while the training of surgeons will typically involve using cadavers before moving on to living patients, the use of Virtual Reality simulations means the need for these methods has been greatly reduced.
In addition to the expected use of VR technology for training simulations, serious gaming has proven an interesting and innovative means of training and educating young doctors. In contrast to the VR simulators, serious games (while, as the name suggests, serious in nature) include more playful aspects, making the learning process more engaging.
From a game designed to help the player learn and understand the processes involved in performing a breast biopsy, to VR technologies being leveraged to improve the preparedness of first responders, VR games have added another effective element to training the modern medical professional. In fact, users have indicated that the playful element of the game actually increases their motivation to play and therefore learn.
VR technology has also been utilized in the training and education of several other medical professionals, including dentists, paramedics, and nursing staff.
Even the seemingly less technical procedures, such as lifting a patient to and from their bed, have been improved thanks to VR technology, ensuring medical staff maintain the correct posture and avoid common work-related injuries in the process.
Diagnostic & Treatment Applications of VR
Virtual Reality has also found a place in diagnostic medicine for various illnesses and disorders. VR procedures such as polygonal modeling allow doctors to observe patients without the process becoming invasive. The virtual models represent realistic and accurate structures, created from real human body scans. This means medical practitioners can examine real organs of the human body and uncover possible traumas or deformities without having to cut someone open.
Further to this, progressive illnesses such as glaucoma can be monitored over a period of time, with the changes observed using VR models better informing the treatment being administered.
How Can AppReal Help?
Virtual Reality applications are among the most groundbreaking and innovative technologies available today. The potential for medical application is staggering, and by further utilizing this technology, both doctors and patients alike can make more accurate and better informed medical decisions, resulting in a higher standard of care and an enhanced quality of life.
AppReal is a boundary pushing mobile app development company. And with a strong background in custom app development to complement our specialist understanding of virtual reality development, our expert team is ready to guide you through this dynamic and fast-moving marketplace.
We can help you take your project from its initial concept through to visual design and technical development, producing a best in class, industry-changing Virtual Reality healthcare app.
Are you ready to make your healthcare VR app a reality? Speak with one of our friendly experts today.